Blood pressure is the amount of pressure the blood exerts on the arterial walls while being pumped throughout the body. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is the most common type of cardiovascular disease, which overworks the heart and hardens the arteries. If untreated, high blood pressure may increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, death, or other serious health implications for those inflicted.1,2 Though individual blood pressure may vary from person to person, a healthy cardiovascular system has blood pressure that rises during physical exertion and decreases while at rest.
Herbs for Hypertension
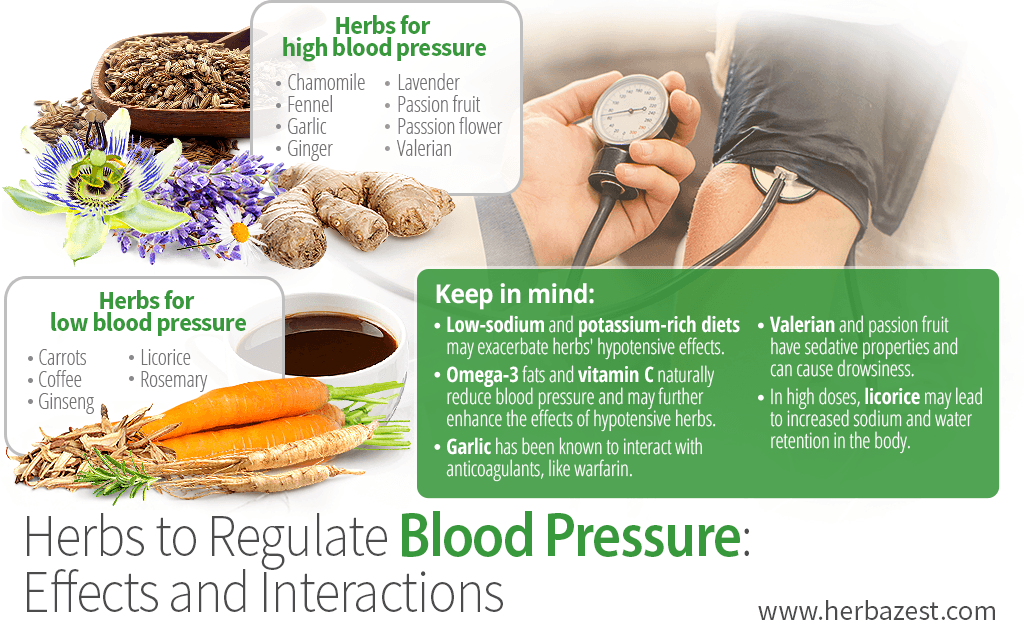
Garlic, ginger, passion fruit, and valerian have all been shown effective in managing high blood pressure. Garlic lowers triglyceride and cholesterol levels to aid in the prevention of adverse, age-related cardiovascular changes; however, it has been known to interact with anticoagulants like warfarin. Ginger root has antispasmodic properties, which help improve blood circulation while relaxing the muscles surrounding the arteries. Using garlic and ginger in healthy, Asian-inspired meal recipes is one great way to reap their hypotensive benefits.
Passion fruit is derived from the passion flower plant and holds the same soothing qualities as the valerian root, which is highly effective in managing the overall stress that can contribute to high blood pressure. Enjoy valerian root and passion fruit in their tea forms, but be mindful of the fact that they are sedatives and may cause drowsiness.
Other popular herbs for high blood pressure, such as chamomile, lavender, and fennel have also been proven to be effective by studies.3
Herbs for Hypotension
Hypotension is defined as blood pressure that is below normal, often occurring when the heart does not pump blood rapidly enough to allow the body to prepare for increased physical activity. Common signs and symptoms of hypotension include dizziness, clammy skin, drowsiness, fainting, loss of vision, nausea, and general fatigue.4
Coffee, rosemary, licorice, ginseng, and carrot, all have antihypotensive properties, raising blood pressure levels in individuals suffering from hypotension.5,6,7 Carotenes in carrots are extremely beneficial in the treatment of hypotension, while antioxidants and caffeine in coffee help prevent heart disease and may produce a hypertensive effect. Though there are many benefits to these methods of approach, it is advisable to use them in moderation. Overconsumption of caffeine may lead to dependency. In addition, licorice - while highly effective for raising blood pressure - may also lead to increased sodium levels and water retention in the body when consumed in high doses.
Herbal Remedies and Medication for Blood Pressure
While garlic is one of the most commonly recommended herbs for treating high blood pressure, it should be noted that a diet high in potassium and low in salt is also known to lower blood pressure. For this reason, certain hypotensive individuals following low-sodium and potassium-rich diets may not fully reap the hypertensive benefits of herbs such as the licorice root, whose effects will be cancelled out by the potassium levels.
Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids and high vitamin C intake are also responsible for a decrease in blood pressure and may worsen the effects of hypotensive herbs and medications.
Diet and exercise, stress reduction, weight management, and other natural treatments play an important role in maintaining a healthy blood pressure. Though no direct cause has been identified for the majority of blood pressure-related health concerns, age, weight, high salt and alcohol intake, poor diet, and genetic predisposition are all important risk factors. Luckily, blood pressure can be effectively managed through the use of some high-quality herbs.
Sources
- International Research Journal of Pharmacy, Hypertension and herbal plants, 2011
- National Institutes of Health, Description of high blood pressure, 2015
- National Toxicology Program, Chemical information review document for valerian, 2009
- Encyclopedia of Herbal Medicine, pp. 369, 524, 525-530, 534, 607-608
- Medicinal Plants of the World, pp. 39, 160, 227, 276, 335, 349, 397, 430
- Pharmacognosy Reviews, Role of natural herbs in the treatment of hypertension, 2011
Footnotes
- Centers fo Disease Control and Prevention. Facts About Hypertension. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from: https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/facts.htm
- MedlinePlus. High blood pressure in adults - hypertension. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000468.htm
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS). (2019). KCNQ5 activation is a unifying molecular mechanism shared by genetically and culturally diverse botanical hypotensive folk medicines. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1907511116
- StatPearls. (2022). Hypotension. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499961/
- Foods. (2020). Assessment of Healthy and Harmful Maillard Reaction Products in a Novel Coffee Cascara Beverage: Melanoidins and Acrylamide. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7278827/
- Journal of Ginseng Research. (2020). Adaptogenic effects of Panax ginseng on modulation of cardiovascular functions. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7322748/
- Journal of Ethnopharmacology. (2014). Effectiveness of Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil as antihypotensive agent in primary hypotensive patients and its influence on health-related quality of life. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24269249/