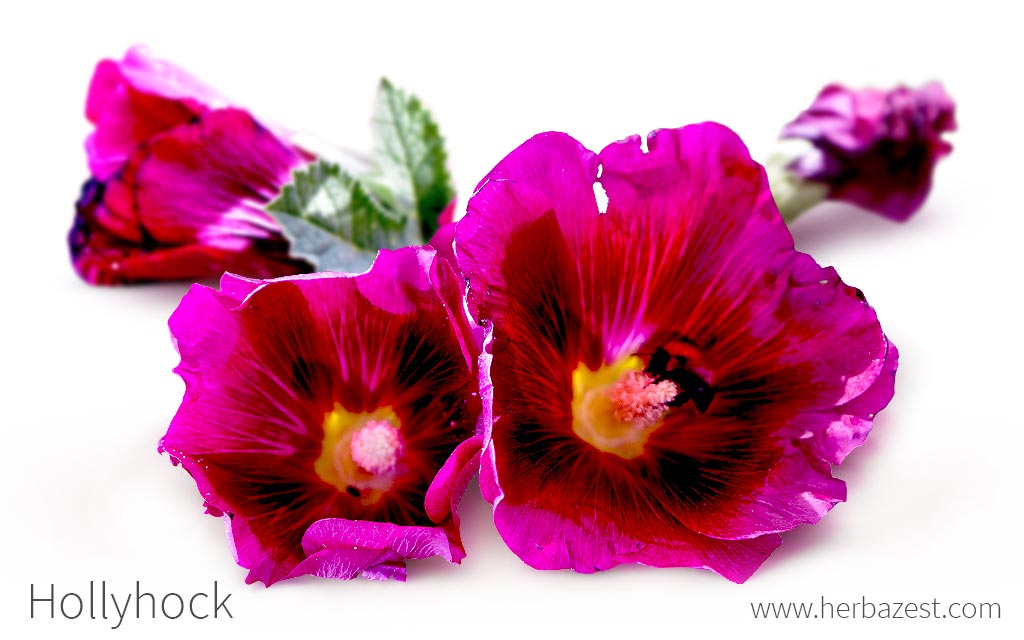
Hollyhock is an attractive flower grown in many gardens across the world. It originated in China and was introduced to Europe in the 15th century. As well as a pretty addition to a flowerbed, hollyhock is widely recognized for its medicinal value, and it is often used as a natural dye in food, cosmetics, and textiles.
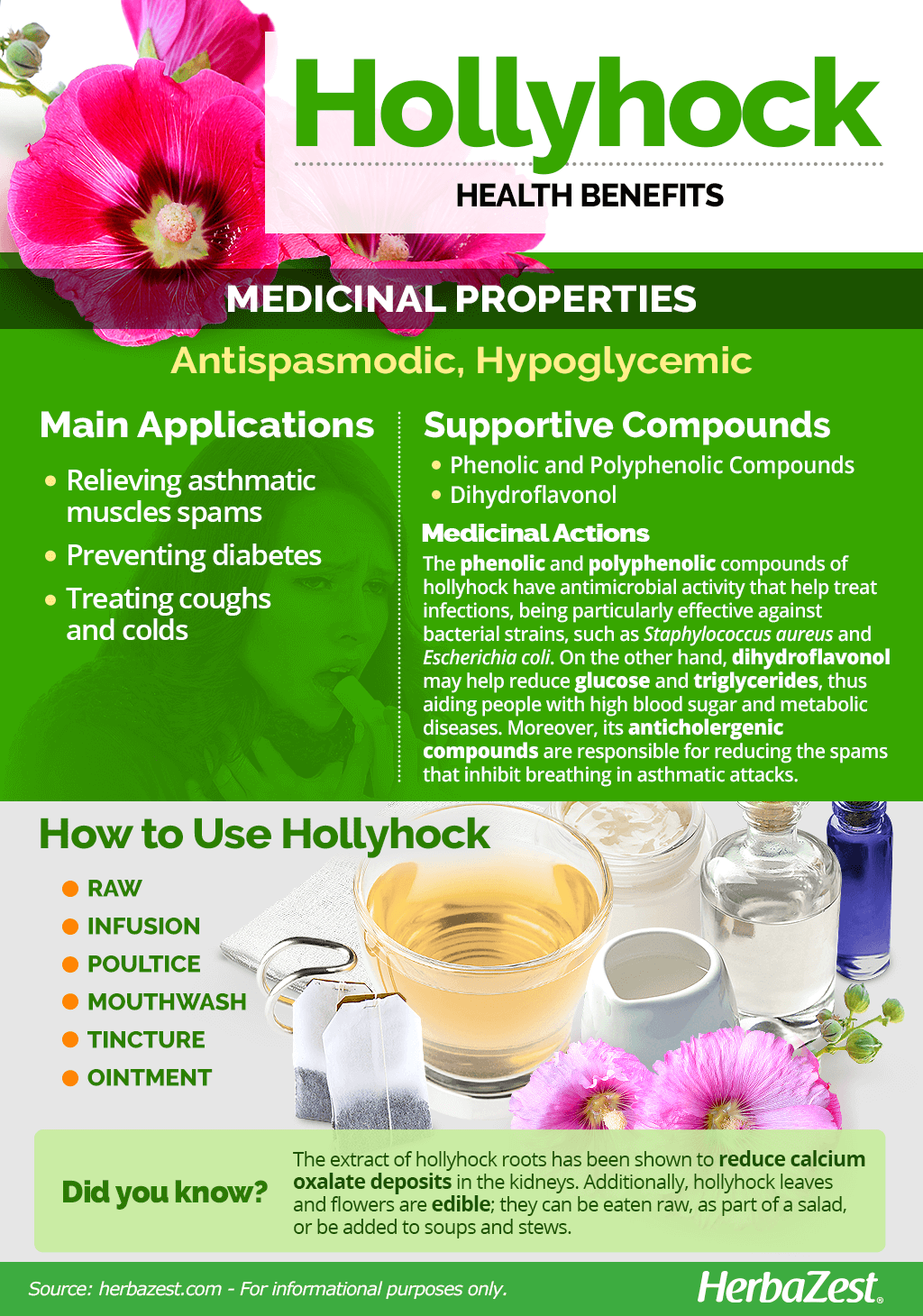
Hollyhock Medicinal Properties
- Medicinal action Antispasmodic, Hypoglycemic
- Key constituents Phenolic and Polyphenolic Compounds, Dihydroflavonol
- Ways to use Hot infusions/tisanes, Food, Tincture, Poultice, Ointment
- Medicinal rating (2) Minorly useful plant
- Safety ranking Safe
Health Benefits of Hollyhock
The Chinese used extract of hollyhock in many traditional remedies, including prescriptions for bronchial complaints, as well as in anti-inflammatory and painkilling preparations. Modern scientific research has revealed that the plant does possess compounds that can have medicinal benefits for the human body. Hollyhock benefits are mainly used for:
- Relieving asthmatic muscle spasms. A substance within the plant can help soothe muscles during an asthma attack, therefore regulating breathing.
Prevent diabetes. Hollyhock contains compounds that can decrease glucose levels, hence reducing the chance of developing diabetes.
- Treating coughs and colds. Components within hollyhock are able to soothe a sore throat and ease the symptoms of the common cold.
Traditional remedies have also used the plant in a variety of treatments, from improving blood circulation to easing labor pains and even preventing miscarriage.
In Tibetan medicine, hollyhock benefits have also been used in therapies for inflammation of the kidneys and womb.
How It Works
Hollyhock is rich in phenolic and polyphenolic compounds, which have antimicrobial activity that can help the body to resist infections. Extracts of hollyhock leaves and flowers have been found to be effective against Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhy, Escherichia coli, and Streptococcus pyogenes, among other bacteria.1
In addition, a chemical called dihydroflavonol - also present in the flower - is thought to be able to decrease glucose and triglycerides levels in humans. This reduction of sugars in the body may help those at risk of diabetes to avert the condition.2
Tests have also been carried out in order to understand the effect hollyhock can have on muscles during an asthma attack. Although the mechanisms are yet to be fully understood, it is thought that its anticholinergic compounds successfully block the impulses that go through the parasympathetic nerves, helping regulate the movement of the respiratory tract muscles and reducing the spasms that inhibit breathing.3
The extract of hollyhock roots has been shown to reduce calcium oxalate deposits in the kidneys.4
Antispasmodic properties can be found in herbs like hepatica and linden, whereas cinnamon and yacon provide hypoglycemic benefits.
Hollyhock Cautions
While hollyhock is considered safe to ingest or use topically, it is recommended to obtain advice from a health professional before regular intake, particularly for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Hollyhock is vulnerable to a disease known as mallow rust, so it is advisable to look for and discard infected leaves or flowers before consuming the plant. Plants should be thoroughly washed and sanitized before consumption, particularly if a synthetic fertilizer has been used during growth, as these can be harmful to the human body.
For those with sensitive skin, hollyhock can cause irritation and dermatitis.
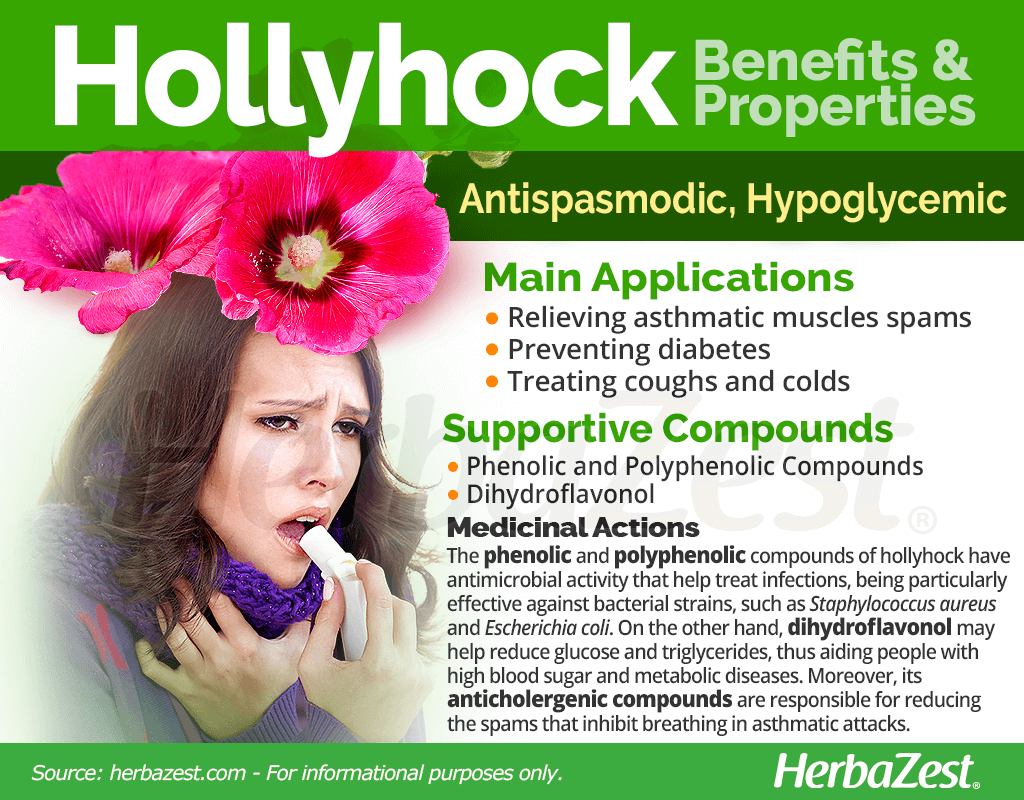
How to Consume Hollyhock
- Edible parts Flowers, Leaves, Stem
- Edible uses Coloring, Beverage
To obtain the medicinal properties of this plant, the most popular ways of consumption are as food or tea. However, hollyhock is also available as a health supplement, and it is possible to use it in medicinal preparations at home.
Most medicinal forms of consuming hollyhock are made from the leaves and flowers of the plants, and sometimes from the stem.
Natural Forms
Raw. Hollyhock leaves and flowers are edible, and they can be added to all kinds of food without altering the predominant flavors of any recipe. They are often eaten raw as part of a salad, but they can also be added to soups and stews for cooking.
Infusion. Tea made from the leaves and flowers can be a convenient way to consume the herb, especially when using it to combat some cold symptoms, such as a sore throat.
Poultice. The flowers, leaves, and stem of the plant can be crushed into a pulp and applied to irritated skin. It is said to relieve sore patches.
Mouthwash. The cold tea mixture can be used as a mouthwash to treat sore and inflamed gums and soothe pain from infections.
Herbal Remedies & Supplements
Tincture. A tincture can be beneficial for quick consumption of hollyhock. A few drops should be diluted into water to drink. This is said to be an efficient way of treating internal inflammation.
Ointment. Hollyhock in this form is intended for topical use; it can soothe skin inflammation caused by rashes and insect bites.
Growing
- Harvested parts Flowers, Leaves, Stem
- Light requirements Full sun
- Soil Well-drained
- Growing habitat Temperate climates
- Planting time Right after last frost
- Plant spacing average 0.6 m (1.97 ft)
- Potential insect pests Japanese beetles
- Potential diseases Rust
- Potential animal pests Chipmunks, Rabbits, Squirrels
Hollyhock is largely considered to be an aesthetically-pleasing flower that is fairly simple to cultivate, making it very popular. It appears in many gardens all over the world, and it needs minimal attention to thrive.
Growing Guidelines
Hollyhock seeds should be sown directly into soil, placed around 30 inches (75 cm) apart. They should not be planted too deep, as the seeds need sunlight to germinate.
The ideal soil for the hollyhock plant to thrive should be rich and well-drained.
The plants should be kept in full sun or partial shade.
They should be sheltered from the wind, or if not, a trellis or support system should be available.
The hollyhock plant will flower between July and September.
- Optimum hardiness zones are 3 - 10.
Additional Information
- Other uses Paper, Dye
Plant Biology
Hollyhock is resistant to a variety of environments, which is why it can be found growing in many different climes. It can be an herbaceous biennial or short-lived perennial, and it is usually between two and nine feet tall (60 - 275 cm), but can reach up to 15 feet (4.6 m) in ideal conditions. The stems are light green, leaves medium green, and flowers can be a range of colors. The flowers can appear individually or in clusters along the stem, and they are often spotted and can have double petals. All parts of the plant have coarse hair on the surface.
Classification
Hollyhock, or Alcea rosea, is part of the Malvaceae or mallow family, which contains 2,300 species spread over 200 genera. This family contains some economically important and well-known herbs, including hibiscus, marsh mallow, mallow, cola nut, and cacao.
An alternative name for the genus Alcea is Althaea, derived from the Greek word althein, which means to heal. This is indicative of the plant's many medicinal properties.
Related Species and Subspecies of Hollyhock
The genus Alcea consists of two species, Alcea rosea and Alcea pallida. Both of these are a popular garden flower. Within the Malvaceae family are three species of marshmallow flowers: palm-leaf marshmallow (Althaea cannabina), hairy marshmallow (Althaea hirsuta), and common marshmallow (Althaea officinalis). The last of these was the original ingredient for production of confectioner's marshmallows.
Historical Information
In 17th century Japan, the founder of the Tokugawa shogunate - the last feudal Japanese military government - insisted on using his own hollyhock emblem instead of the traditional imperial emblem of the chrysanthemum to reiterate his opposition to the political power of the Emperor.
It is evident that the plant was introduced to Europe before this time, however, as it can be seen in many 15th century German paintings. By the 18th century, in Germany, hollyhock had become so popular that the poet Goethe had cultivated a vast amount, and he even threw tea parties in its honor.
Economic Data
Hollyhock can be grown in most countries; therefore it is not necessary to import the leaves and flowers for general consumption. Although it is not as commercially significant as other medicinal herbs, hollyhock is being cultivated in vast quantities in the Balkans for the pharmaceutical industry.
Popular Beliefs
In Kyoto, Japan, every year in May there is a large and important festival called the aoi matsuri. This translates to hollyhock festival. At the event, hollyhock leaves are used as the main decoration, as they are said to protect against storms and evil. This celebration has taken place annually since the 6th century.
Other Uses
Dye. The hollyhock flowers contain an anthocyanin pigment that can be extracted and used as dye in food and drink products such as jams, candies, and wine. The brown pigment can also be obtained to measure pH levels.
Paper. Hollyhock's stem fibers are used in paper manufacture.
Hollyhock has long been valued for its medicinal properties, and it can be used in a variety of ways to treat a wide range of conditions. Easy to cultivate, it is a recommended addition to the garden, as it is both attractive and useful.
Sources
- Balkan Ecology Project
- Edible & Medicinal Flowers, pp. 43
- Edible Medicinal And Non-Medicinal Plants, pp. 292-297
- Garden Flora: The Natural and Cultural History of the Plants In Your Garden, pp. 40-42
- Handbook on Medicinal Herbs with Uses, pp. 70
- Living with Herbs, pp. 165-167
- Medicinal Properties of Herbs and Plants
- National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, Hypoglycemic activity evaluation and chemical study on hollyhock flowers
Footnotes:
- China Journal of Chicnese Materia Medica (Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi).(2015). Study on composition, antibiotic activity and antioxidant activity of volatile oils from uyghur medicine Althaea rosea. Retrieved January 13, 2023, from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26281609/
- Fitoterapia. (2015). Hypoglycemic activity evaluation and chemical study on hollyhock flowers. Retrieved January 13, 2023, from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25677352/
- Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. (2019). Pharmacological basis for the medicinal use of Alcea rosea in airways disorders and chemical characterization of its fixed oils through GC-MS. Retrieved January 13, 2023, from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31894065/
- Indian Journal of Pharmacology. (2012). Alcea rosea root extract as a preventive and curative agent in ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis in rats. Retrieved January 13, 2023, from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3371449/